Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Tanaka, Nobuyuki; Sawada, Shinichi*; Yamaki, Tetsuya*; Kodaira, Takahide*; Kimura, Takehiro*; Nomura, Mikihiro*
Chemical Engineering Science, 237, p.116575_1 - 116575_11, 2021/06
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:5.78(Engineering, Chemical)We have been developing the ion exchange membranes by a radiation grafted polymerization method to improve HI concentration performance for Electro-electrodialysis (EED) in the thermochemical water-splitting hydrogen production iodine-sulfur process. In this work, the crosslinking structures were introduced to the ion exchange membranes. The proton conductivity ( ), transport number (t
), transport number (t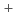 ), and water permeation factor (
), and water permeation factor ( ) of these crosslinked ion exchange membranes were measured and the effect of crosslinks to these performance indexes were investigated. The introduction of crosslinks was found to improve the selectivity of H
) of these crosslinked ion exchange membranes were measured and the effect of crosslinks to these performance indexes were investigated. The introduction of crosslinks was found to improve the selectivity of H and water transport (increase of t
and water transport (increase of t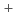 and decrease of
and decrease of  ), although the
), although the  somewhat decreased. The EED model that we established to discuss the permeation mechanism of EED system was used to theoretically analyze the effect of crosslink on the performance indexes. Based on this analysis of measurement results, the introduction of the crosslink was found to little affect the absorbed amount of HIx solution and H
somewhat decreased. The EED model that we established to discuss the permeation mechanism of EED system was used to theoretically analyze the effect of crosslink on the performance indexes. Based on this analysis of measurement results, the introduction of the crosslink was found to little affect the absorbed amount of HIx solution and H diffusion coefficient in the tested membranes, whereas it could lead to decrease I
diffusion coefficient in the tested membranes, whereas it could lead to decrease I diffusion coefficient. The results of
diffusion coefficient. The results of  and t
and t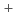 could reflect these effects. In addition, we found the fact that crosslink can inhibit the swelling due to the absorption of the HIx solution. As a result, the
could reflect these effects. In addition, we found the fact that crosslink can inhibit the swelling due to the absorption of the HIx solution. As a result, the  value decreased owing to the introduction of crosslink.
value decreased owing to the introduction of crosslink.
Shiga, Motoyuki
Reference Module in Chemistry, Molecular Sciences and Chemical Engineering (Internet), 22 Pages, 2018/00
Nuclear quantum effects are important in molecular systems containing light elements such as hydrogen. For example large zero vibration and proton tunneling in hydrogen bonded systems originate from nuclear quantum effects. We herein describe path integral molecular dynamics (PIMD) where nuclear quantum effects are taken into account based on imaginary time path integral theory. PIMD provides numerically exact solutions for quantum statistics of complex molecular systems in thermal equilibrium. Centroid and ring polymer molecular dynamics are extensions to provide approximate quantum dynamics. Combination with ab initio electronic structure calculations enables simulation of the whole entity of many-electron many-nuclei systems.
Segawa, Tomoomi; Fukasawa, Tomonori*; Huang, A.-N.*; Yamada, Yoshikazu; Suzuki, Masahiro; Fukui, Kunihiro*
Chemical Engineering Science, 153, p.108 - 116, 2016/10
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:26.31(Engineering, Chemical)The influence of the heating method and rate on the morphology of CuO powders synthesized from Cu(NO )
)
 3H
3H O aqueous solutions by denitration was investigated. The median diameter of the obtained powder was found to decrease as the heating rate increased, independent of the heating method. The microwave heating method remarkably reduced the particle size and enhanced the irregularity and disorder of the shape and surface of the particles, which were found to be more widely distributed. In contrast, the microwave hybrid heating method yielded the most spherical particles with the smoothest surface. It was also found that this heating method sharpened the particle size distribution and had higher energy efficiency than the MW method. Numerical simulations also indicated a difference in the energy efficiency between these two methods. The simulations also revealed that the hybrid method could heat the whole reactor more uniformly with a lower microwave output.
O aqueous solutions by denitration was investigated. The median diameter of the obtained powder was found to decrease as the heating rate increased, independent of the heating method. The microwave heating method remarkably reduced the particle size and enhanced the irregularity and disorder of the shape and surface of the particles, which were found to be more widely distributed. In contrast, the microwave hybrid heating method yielded the most spherical particles with the smoothest surface. It was also found that this heating method sharpened the particle size distribution and had higher energy efficiency than the MW method. Numerical simulations also indicated a difference in the energy efficiency between these two methods. The simulations also revealed that the hybrid method could heat the whole reactor more uniformly with a lower microwave output.
Nakahara, Masaumi; Nomura, Kazunori
Chemical Engineering Science, 66(4), p.740 - 746, 2011/02
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:26.43(Engineering, Chemical)Counter current experiments in a single cycle solvent extraction system were carried out with centrifugal contactors to study flow rate reductions in extraction solvent and stripping solution with a dissolver solution of irradiated mixed oxide fuel. Uranium and Pu leaked to the raffinate with a 15% decrease in the extraction solvent flow rate, which brought about an accumulation of U and Pu in the co-decontamination section. On the other hand, a 15% decrease in the stripping solution flow rate did not affect the stripping of U and Pu so greatly.
Nagame, Yuichiro; Haba, Hiromitsu*
Encyclopedia of Chemical Sciences, Engineering and Technology Resources (Internet), 76 Pages, 2008/00
This article gives a brief summary of the reported syntheses and nuclear properties of the transactinide elements as well as chemical investigation of those elements. Experimental techniques of single atom detection after in-flight separation with electromagnetic separators have made a breakthrough in production and identification of new transactinide nuclides. Development of automated rapid chemical separation techniques based on one atom-at-a-time scale has also considerably contributed to the progress of chemical studies of the transactinide elements. Some key experiments exploring new frontiers of the production and chemical characterization of the transactinide elements as well as the state of the art in these experimental studies are demonstrated. Prospects of extending nuclear and chemical studies of the heaviest elements in near future are shortly considered.
Nomura, Mikihiro*; Okuda, Hiroyuki; Kasahara, Seiji; Nakao, Shinichi*
Chemical Engineering Science, 60(24), p.7160 - 7167, 2005/12
Times Cited Count:29 Percentile:65.93(Engineering, Chemical)The Bunsen reaction (SO +I
+I +2H
+2H O=H
O=H SO
SO +2HI) in the water-splitting IS process was examined using an electrochemical cell with a cation exchange membrane. The optimal molalities of anolyte and catholyte were evaluated by total thermal efficiency. The I
+2HI) in the water-splitting IS process was examined using an electrochemical cell with a cation exchange membrane. The optimal molalities of anolyte and catholyte were evaluated by total thermal efficiency. The I /HI ratio had little effect on the required total voltage; the I
/HI ratio had little effect on the required total voltage; the I /HI ratio can be reduced to 0.5 without decreasing the efficiency. HI and H
/HI ratio can be reduced to 0.5 without decreasing the efficiency. HI and H SO
SO molality greatly affected the efficiency. Membrane resistances are very important parameters affecting the efficiency. The total thermal efficiency increased by 3.0% by increasing the operating temperature from 313K to 363K.
molality greatly affected the efficiency. Membrane resistances are very important parameters affecting the efficiency. The total thermal efficiency increased by 3.0% by increasing the operating temperature from 313K to 363K.